A stock has a beta of 1.15 – When it comes to investing, understanding a stock’s beta is crucial. A stock with a beta of 1.15, as we will explore in this article, provides valuable insights into its volatility and risk profile, helping investors make informed decisions.
Beta, a measure of a stock’s sensitivity to market fluctuations, plays a significant role in portfolio management and stock selection. Let’s delve into the implications of a stock’s beta of 1.15 and how it can guide investment strategies.
Beta Definition
Beta is a measure of the volatility of a stock compared to the overall market. It is calculated by dividing the covariance of the stock’s returns with the covariance of the market returns. A beta of 1 means that the stock moves in line with the market.
A beta greater than 1 means that the stock is more volatile than the market, while a beta less than 1 means that the stock is less volatile than the market.
Calculating Beta
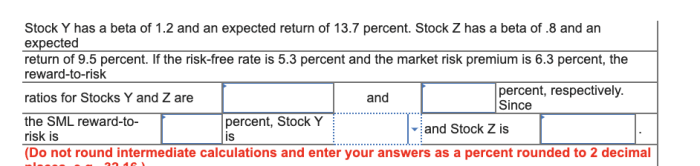
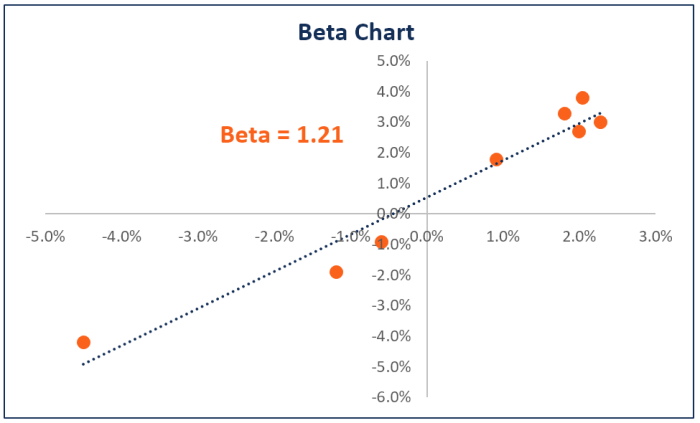
Beta is calculated using the following formula:“`Beta = Covariance(Stock Returns, Market Returns) / Variance(Market Returns)“`For example, if the covariance between the stock’s returns and the market returns is 0.15 and the variance of the market returns is 0.09, then the beta of the stock would be 1.67. This means that the stock is 67% more volatile than the market.
Interpreting Beta
Beta is a useful tool for investors to assess the risk of a stock. A stock with a high beta is considered to be more risky than a stock with a low beta. This is because a stock with a high beta is more likely to experience large price swings.
Investors who are willing to take on more risk may choose to invest in stocks with high betas, while investors who are more risk-averse may choose to invest in stocks with low betas.
Beta Value Interpretation: A Stock Has A Beta Of 1.15

A stock’s beta value provides insights into its volatility and risk relative to the overall market. In this case, a beta of 1.15 suggests that the stock is slightly more volatile than the broader market.
Implications of Beta Value
A beta value of 1.15 indicates that the stock tends to move in the same direction as the market, but with slightly greater amplitude. When the market rises, the stock is likely to experience a slightly larger percentage gain. Conversely, during market downturns, the stock may experience a slightly larger percentage loss.
This means that the stock carries a higher level of systematic risk compared to the market as a whole.
Beta and Portfolio Management

Beta is a crucial metric for managing investment portfolios. It helps investors understand the risk-return relationship of individual stocks and optimize their portfolio’s overall risk exposure.
By diversifying portfolios based on beta values, investors can reduce their portfolio’s volatility and enhance its overall return potential.
Diversifying Portfolios Based on Beta Values
Investors can diversify their portfolios by combining stocks with different beta values. This strategy helps balance the risk and return of the portfolio. Here’s how:
- Combining High-Beta and Low-Beta Stocks:Combining high-beta stocks with low-beta stocks can create a portfolio with a moderate overall beta. This approach balances the higher potential returns of high-beta stocks with the lower volatility of low-beta stocks.
- Matching Beta to Risk Tolerance:Investors should align their portfolio’s beta with their risk tolerance. Risk-averse investors may prefer portfolios with low beta values, while risk-tolerant investors may seek higher beta portfolios.
- Sector Diversification:Beta values can also vary across sectors. Diversifying across sectors with different betas can further reduce portfolio risk.
Beta and Stock Selection
Beta is a crucial factor to consider when selecting stocks, as it helps investors assess the stock’s volatility and risk in relation to the overall market. By understanding the beta value of a stock, investors can make informed decisions about whether it aligns with their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Using Beta to Identify Stocks
Investors can use beta to identify stocks that align with their risk tolerance. Stocks with a beta greater than 1 are considered more volatile than the market and have the potential for higher returns, but also carry greater risk. Conversely, stocks with a beta less than 1 are less volatile than the market and have lower potential returns but also lower risk.Investors
with a high risk tolerance may prefer stocks with higher betas, as they offer the potential for greater returns. However, investors with a low risk tolerance should consider stocks with lower betas, as they provide more stability and lower potential losses.
Beta and Industry Analysis
Beta is a valuable tool for analyzing the risk and return profiles of different industries. Industries with high betas tend to be more volatile and have higher expected returns, while industries with low betas tend to be less volatile and have lower expected returns.
Examples of Industry Beta Analysis, A stock has a beta of 1.15
For example, the technology industry has historically had a high beta, reflecting the high volatility of technology stocks. This is because technology companies are often subject to rapid technological changes and intense competition. As a result, technology stocks tend to experience large swings in price, both up and down.
If a stock has a beta of 1.15, it’s more volatile than the overall market. To learn more about beta and other investment terms, check out our unit 2 vocabulary level c . Understanding these concepts will help you make informed investment decisions.
In contrast, the utility industry has historically had a low beta, reflecting the low volatility of utility stocks. This is because utility companies are typically regulated and have stable earnings. As a result, utility stocks tend to experience smaller swings in price.
Beta Limitations
Beta is a useful measure of stock risk, but it has some limitations that investors should be aware of. These limitations include:
Factors Influencing Beta
Beta is not a constant value and can change over time. This is because beta is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- The company’s industry
- The company’s size
- The company’s financial leverage
- The overall market conditions
It is important to consider these factors when using beta to assess stock risk.
Beta and Diversification
Beta is a measure of systematic risk, which is the risk that cannot be diversified away. However, it is important to note that beta does not measure unsystematic risk, which is the risk that can be diversified away. This means that investors should not rely solely on beta when making investment decisions.
User Queries
What is the significance of a stock’s beta?
Beta measures the sensitivity of a stock’s price to market fluctuations, indicating its volatility and risk compared to the broader market.
How is beta calculated?
Beta is calculated by comparing the historical returns of a stock to the returns of a market index, such as the S&P 500.
What does a beta of 1.15 imply?
A beta of 1.15 suggests that the stock is 15% more volatile than the market. When the market rises by 1%, the stock is expected to rise by 1.15%.
How can investors use beta in portfolio management?
Beta can be used to diversify portfolios by combining stocks with different betas. This helps reduce overall portfolio risk and volatility.
What role does beta play in stock selection?
Investors can use beta to identify stocks that align with their risk tolerance. Stocks with higher betas offer higher potential returns but also greater risk, while stocks with lower betas provide more stability.