The Earth Layers Foldable Answer Key embarks on an enlightening journey into the heart of our planet, unraveling the intricate tapestry of its composition. This comprehensive guide unveils the secrets of the Earth’s layered structure, providing a tangible representation of its complexities.
Delving into the depths of the Earth, we explore the characteristics and composition of each layer, from the enigmatic crust to the molten core. The foldable answer key serves as a visual masterpiece, offering a dynamic and interactive understanding of the Earth’s enigmatic architecture.
Earth’s Layered Structure
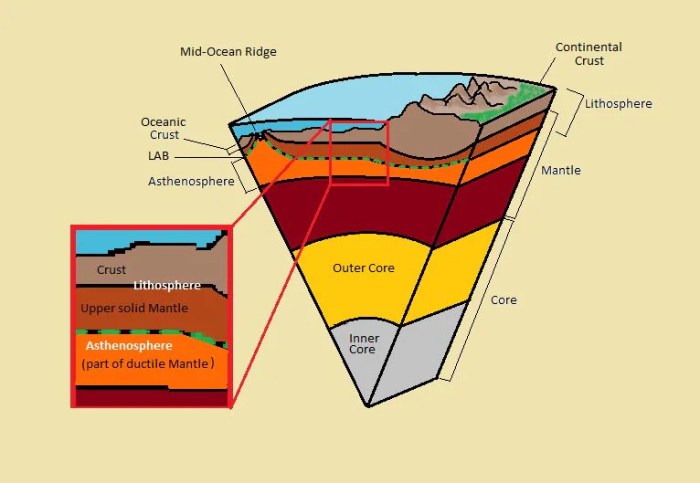
The Earth’s interior is composed of distinct layers, each with its unique physical and chemical properties. This layered structure has been determined through various geophysical techniques, including seismic wave analysis and gravity measurements.
The Earth’s layers can be broadly classified into three major zones: the crust, mantle, and core.
The Crust
The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, ranging in thickness from a few kilometers beneath the oceans to over 100 kilometers beneath the continents. It is primarily composed of silicate minerals and is divided into two main types:
- Continental Crust:Found beneath the continents, it is thicker and less dense than oceanic crust, with an average thickness of 35 kilometers.
- Oceanic Crust:Forms the ocean floor, is thinner and denser than continental crust, with an average thickness of 7 kilometers.
Crust: The Earth Layers Foldable Answer Key
The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, forming a thin, solid shell that encloses the planet. It is composed primarily of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks.
There are two main types of crust: oceanic and continental.
Oceanic Crust
- Oceanic crust is found beneath the oceans and is typically thinner than continental crust, with an average thickness of around 5-10 km.
- It is composed primarily of mafic rocks, such as basalt and gabbro, which are rich in iron and magnesium.
- Oceanic crust is constantly being created at mid-ocean ridges, where new magma rises from the mantle and solidifies.
- As the oceanic crust moves away from the mid-ocean ridge, it cools and becomes denser, eventually sinking back into the mantle at subduction zones.
Continental Crust
- Continental crust is found beneath the continents and is thicker than oceanic crust, with an average thickness of around 30-50 km.
- It is composed primarily of felsic rocks, such as granite and gneiss, which are rich in silica and aluminum.
- Continental crust is formed through the melting and differentiation of the mantle, followed by the accumulation of the resulting magma on the surface.
- Continental crust is much older than oceanic crust, with some continental crustal rocks dating back to over 4 billion years.
Mantle
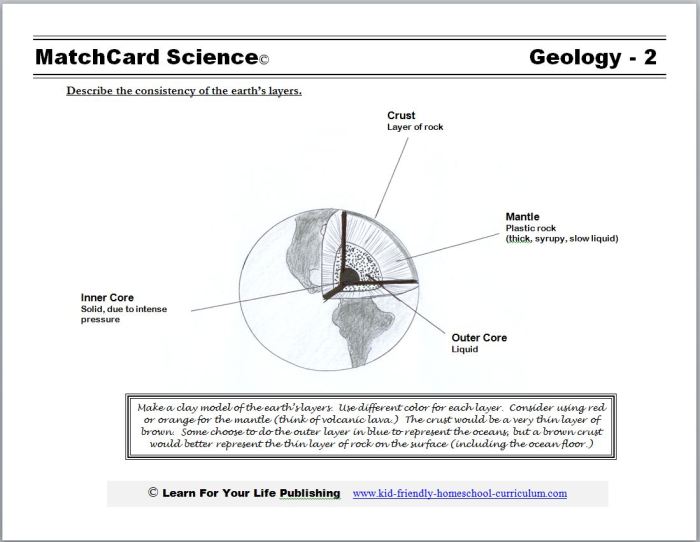
The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth, located between the crust and the core. It extends from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) and makes up about 84% of the Earth’s volume.
The mantle is composed primarily of solid rock, but it is not as rigid as the crust. It is made up of a mixture of silicate minerals, including olivine, pyroxene, and garnet. The mantle is extremely hot, with temperatures ranging from about 1,000 degrees Celsius (1,832 degrees Fahrenheit) at the base of the crust to about 3,700 degrees Celsius (6,692 degrees Fahrenheit) at the boundary with the core.
The mantle is divided into two main layers: the upper mantle and the lower mantle. The upper mantle is about 700 kilometers (435 miles) thick and is less dense than the lower mantle. The lower mantle is about 2,200 kilometers (1,367 miles) thick and is denser than the upper mantle.
Role of the Mantle in Plate Tectonics
The mantle plays an important role in plate tectonics. The heat from the mantle causes the rock in the mantle to flow slowly. This flow of rock drives the movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates.
The mantle is also responsible for the formation of volcanoes and earthquakes. Volcanoes are formed when magma from the mantle rises to the surface of the Earth. Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates along the boundaries between them.
4. Core
The Earth’s core is the innermost layer of the Earth and is primarily composed of iron and nickel. It is divided into two distinct regions: the inner core and the outer core.
Inner Core
The inner core is a solid sphere with a radius of approximately 1,220 kilometers. It is extremely dense and has a temperature of about 5,200 degrees Celsius, which is comparable to the surface temperature of the Sun.
Outer Core
The outer core is a liquid layer that surrounds the inner core. It is less dense than the inner core and has a temperature of about 4,400 degrees Celsius. The outer core is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
Foldable Answer Key
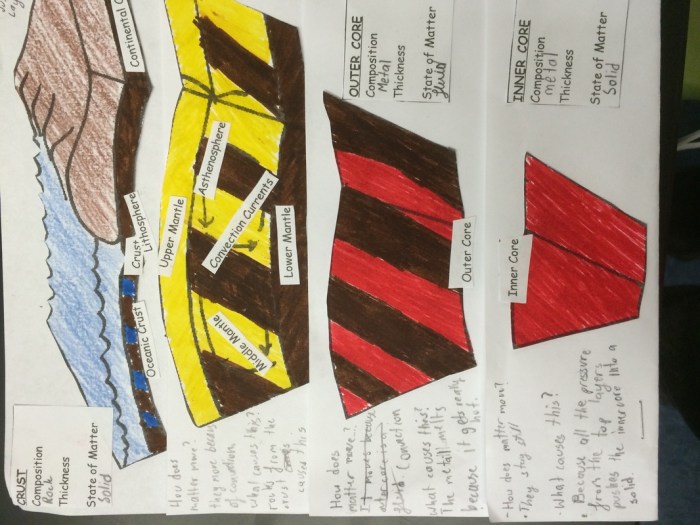
A foldable answer key is a visual representation of the Earth’s layers that can be used to reinforce students’ understanding of the topic. It is a fun and engaging way to review the material and can be used as a study tool or assessment.
Creating the Foldable, The earth layers foldable answer key
To create a foldable answer key, follow these steps:
- Start with a piece of paper that is at least 8.5 x 11 inches.
- Fold the paper in half lengthwise.
- Unfold the paper and fold it in half widthwise.
- Unfold the paper and fold it in half diagonally from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.
- Unfold the paper and fold it in half diagonally from the top right corner to the bottom left corner.
- You should now have a square with eight sections.
- Label each section with one of the Earth’s layers: crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
- Add additional information to each section, such as the thickness, composition, and temperature of each layer.
Additional Information
The study of the Earth’s layers is a fascinating and complex field. There are many resources available to help you learn more about this topic.
Here are some additional resources for further exploration:
- USGS: What are the layers of the Earth?
- National Geographic: Earth’s Structure
- NASA: Layers of the Earth
Interesting Facts
- The Earth’s crust is the thinnest layer, with an average thickness of only about 30 miles.
- The mantle is the largest layer, accounting for about 84% of the Earth’s volume.
- The core is the hottest layer, with temperatures reaching up to 9,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
Quick FAQs
What are the main layers of the Earth?
The Earth consists of three primary layers: the crust, mantle, and core.
How does the foldable answer key help in understanding Earth’s layers?
The foldable answer key provides a visual representation of the Earth’s layers, making it easier to comprehend their relative positions and characteristics.
What is the significance of the mantle in plate tectonics?
The mantle plays a crucial role in plate tectonics, as it allows tectonic plates to move and interact, shaping the Earth’s surface.
