Please categorize the statements about slime molds and water molds. – Delving into the realm of “please categorize the statements about slime molds and water molds,” this comprehensive guide embarks on a journey to elucidate the defining characteristics, ecological roles, and comparisons between these fascinating organisms. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of slime molds and water molds, exploring their significance in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Slime molds, enigmatic creatures that defy conventional classification, and water molds, often overlooked yet ecologically vital, take center stage in this discourse. Through detailed descriptions, illustrative examples, and insightful comparisons, we aim to shed light on their unique adaptations and ecological contributions.
Slime Molds: Please Categorize The Statements About Slime Molds And Water Molds.

Slime molds, also known as plasmodial slime molds, are fascinating organisms that exhibit a unique combination of animal and fungal characteristics. These enigmatic creatures belong to the phylum Mycetozoa and are characterized by their ability to exist in two distinct life stages: a vegetative, mobile stage known as the plasmodium and a reproductive, spore-producing stage.
During the vegetative stage, slime molds form a large, multinucleated mass of cytoplasm that resembles a slug or amoeba. This plasmodium can grow to several centimeters in size and move slowly through its environment, feeding on bacteria, fungi, and other organic matter.
As the plasmodium matures, it differentiates into a fruiting body, which produces spores that are dispersed by wind or animals.
Slime molds play an important ecological role in forests and other ecosystems. They are voracious predators of bacteria and fungi, helping to control their populations. Additionally, slime molds contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the soil.
Examples of Slime Mold Species, Please categorize the statements about slime molds and water molds.
- Physarum polycephalum: A common slime mold species found in forests and grasslands worldwide.
- Dictyostelium discoideum: A slime mold species that has been extensively studied in the laboratory.
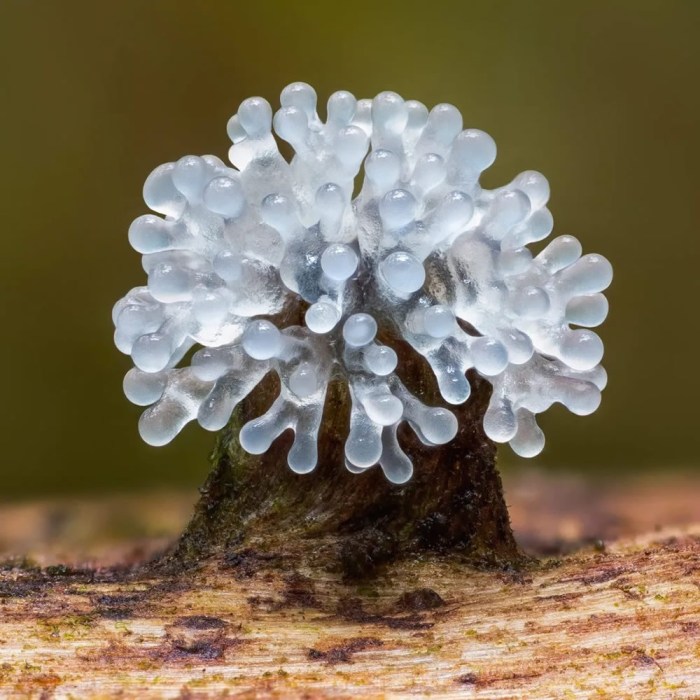
- Fuligo septica: A slime mold species that is known for its large, bright yellow fruiting bodies.
Water Molds

Water molds, also known as oomycetes, are a group of fungus-like organisms that are closely related to true fungi but have evolved to live in aquatic environments. These organisms are found in freshwater and marine habitats and play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling.
Water molds are characterized by their filamentous growth habit, which is similar to that of true fungi. However, unlike true fungi, water molds have cell walls made of cellulose rather than chitin. Additionally, water molds produce motile spores that are dispersed through water, allowing them to colonize new habitats.
Water molds are important decomposers in aquatic ecosystems, breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the water column. Some water mold species are also parasites of plants and animals, causing diseases such as potato blight and fish mold.
Examples of Water Mold Species
- Saprolegnia: A water mold species that is commonly found on dead fish and other aquatic organisms.
- Phytophthora infestans: A water mold species that causes potato blight, a devastating disease of potato crops.
- Achlya: A water mold species that is found in freshwater habitats and is a common parasite of fish.
Comparison of Slime Molds and Water Molds
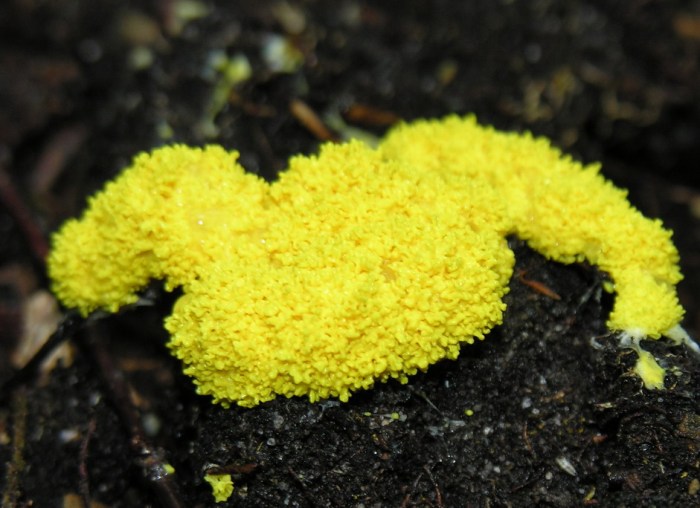

| Characteristic | Slime Molds | Water Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Terrestrial | Aquatic |
| Cell wall composition | Cellulose | Chitin |
| Motility | Yes (plasmodium stage) | No |
| Spore dispersal | Wind or animals | Water |
| Ecological role | Predators of bacteria and fungi, decomposers | Decomposers, parasites |
Slime molds and water molds are both important members of their respective ecosystems. Slime molds play a role in nutrient cycling and decomposition in terrestrial environments, while water molds perform similar functions in aquatic ecosystems.
Questions and Answers
What are the key differences between slime molds and water molds?
Slime molds are terrestrial organisms that exhibit a unique life cycle involving both amoeboid and plasmodial stages, while water molds are aquatic fungi that primarily exist in freshwater environments.
What ecological roles do slime molds play?
Slime molds contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter, and some species exhibit predatory behavior, regulating microbial populations in soil ecosystems.
How are water molds significant in aquatic ecosystems?
Water molds play crucial roles in nutrient cycling, particularly in the decomposition of organic matter, and they can also serve as parasites, affecting fish and other aquatic organisms.